The liver is an external secretion gland and the largest organ in the body. Its mass depends on age and build, but on average it is 1.3-1.5 kg in adults. The liver is located on the right side of the abdominal cavity, just below the diaphragm. It is often called the “second heart” because of its importance to the health of most organs and systems. However, liver diseases can severely impact its function, leading to a range of complications throughout the body.
Why do liver diseases develop?
Liver disease can develop as a result of:
- poor diet,
- alcohol consumption,
- metabolic disorders,
- hereditary predisposition,
- and infections, particularly viral hepatitis (A, B, C, D, E),
- autoimmune hepatitis;
- parasites (e.g., they are the source of such problems as giardiasis, ascariasis, echinococcosis, amebiasis),
- liver blood flow disorders, e.g. cardiovascular failure, hepatic vein thrombosis,
- bile flow disorders,
- blockage of the bile duct by a stone.
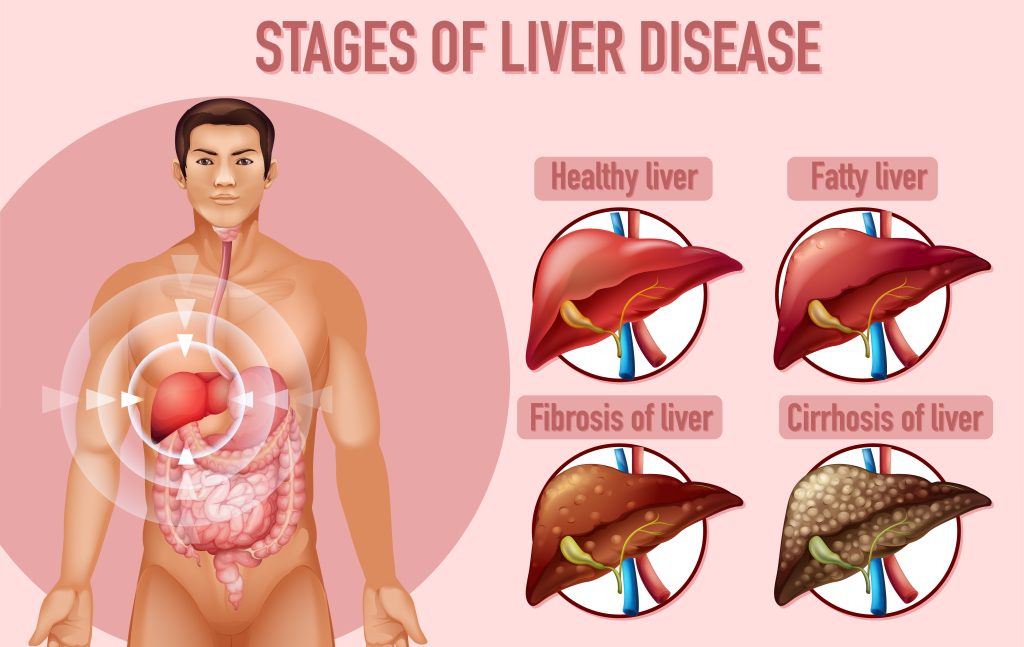
Excessive accumulation of fat in the liver, cholesterol in the liver cells (fatty hepatosis, steatosis), alcohol or viral infections can cause inflammation. This leads to the development of fibrosis, a process in which healthy liver tissue is replaced by scar tissue. Scarring reduces liver function, which has a negative effect on the whole body.
How to diagnose liver diseases?
Harmful habits and improper nutrition provoke liver diseases. On the one hand, this organ quickly recovers with careful treatment, but on the other hand, some diseases easily acquire a chronic character.
How to understand that there are malfunctions in the liver?
- Pain or heaviness in the right subcostal region
The liver is surrounded by a shell, the so-called capsule, which is sensitive to changes in the size of the organ. Inflammation caused by alcohol or excessive fat intake causes the gland to enlarge.
- Weight gain
The liver is involved in the metabolism of fats and carbohydrates. Lack of exercise and too much caloric food cause the liver to fail to process fats and carbohydrates. The excess is deposited as fat in the liver and subcutaneous fatty tissue.
- Nausea or vomiting
When the liver cannot handle toxins, their amount in the blood rises. Excessive amounts of endogenous and exogenous toxins lead to the development of unpleasant symptoms such as nausea and vomiting.
- Increased fatigue
Increased fatigue accompanied by poor performance is closely related to liver disease and is the most frequent and early symptom of hepatic pathologies. Inflammatory substances formed in hepatocytes can affect the transmission of nerve signals in the brain. This leads to the development of increased fatigue and decreased mood.
- Bad breath
Bad breath can indicate a disorder of the digestive system. A sweetish “mouse flavor” can appear when liver cells fail to process toxic substances.

- Yellowing of the skin and eyes
A change in the normal color of the eyes, skin and mucous membranes to a yellow color is called jaundice. This condition is due to excess bilirubin, a yellow pigment that is formed by the breakdown of hemoglobin, entering the bloodstream.
Jaundice may indicate hepatocyte dysfunction and may be a symptom of alcohol-induced pathology.
- Changes in the color of urine and feces
Bilirubin, a yellow pigment and one of the main components of bile, is present not only in the blood, but also in urine and feces. Bilirubin is excreted with bile into the duodenum and changes color to brown when exposed to intestinal bacteria. This brown pigment is what gives the feces its characteristic color. In urine, however, there is another product of bilirubin metabolism, giving it a light yellow color.
- Swelling of the legs
Sometimes liver disease is not recognized until late stages, such as cirrhosis, when the normal liver tissue is replaced by connective tissue.
Swelling of the legs occurs as a result of increased pressure in the vessels of the gland and insufficient formation of the protein albumin. In albumin deficiency, fluid is not retained in the bloodstream and fills the tissues.
- Rapid appearance of bruising
The most important function of the organ is protein formation. In response to chronic alcohol consumption or viruses, the liver stops doing its job and begins to synthesize fewer proteins that regulate blood clotting. As a result, hemorrhagic syndrome develops. Its manifestations are gratuitous bruising, bleeding gums and nosebleeds.
- Pruritus
Itching is a symptom of allergic diseases and liver problems. Itching occurs in response to the irritating effect of excessive bile acids on the skin. It is not uncommon for skin itching and jaundice to go hand in hand or for itching to precede jaundice.
Each of these signs requires a prompt visit to a general practitioner, who will prescribe the necessary types of tests. Further treatment is under the supervision of a gastroenterologist or hepatologist
How to avoid liver diseases
Often liver diseases do not manifest themselves for a long time (perhaps even years). Do you want to stay healthy? Then you need to eliminate external negative factors affecting the liver:
- excessive fatty foods in the diet,
- abuse of alcohol and foods containing a lot of spices, viral attacks,
- uncontrolled intake of medications (especially nowadays, with the new coronavirus infection, taking antiviral drugs and antibiotics).
When should I see an infectious disease specialist?
- If there are the following symptoms: weakness, fatigue, nausea, decreased appetite, sleep disturbance, heaviness in the right subcostal region, joint pain, skin itching, yellowing of the skin and eyes.
- With an increase in the biochemical blood test of ALT, AST, bilirubin, GGTP, alkaline phosphatase. ALT serves as the main marker of inflammation of hepatic tissue.
- When hepatitis B, C viruses (or markers of other viral hepatitis) are detected in the blood.
- When changes in the liver detected by ultrasound (diffuse changes in the liver parenchyma, steatosis, fibrosis, cirrhosis).
- If there have been medical manipulations in the last five years: surgeries (including dental), blood transfusions, endoscopic manipulations, visits to tattoo and manicure salons.